Configuration
Settings that affect your entire site can be changed in 11ty’s configuration file: eleventy.js found in the root of your project, and in _data/site.yml. If you don’t have this file you’ll need to copy or create one using the theme’s default eleventy.js as a base and the default site.yml.
Take a moment to look over the configuration file included with the theme. Comments have been added to provide examples and default values for most settings. Detailed explanations of each can be found below.
Site settings
Most of these settings are found in _data/site.yml.
Skin
To change the “skin”, you need to edit /assets/css/main.css:
@import "../../_sass/minimal-mistakes/skins/default"; // skin
@import "../../_sass/minimal-mistakes"; // main partialsHere you change default to another skin. You can choose between “default”, “air”, “aqua”, “contrast”, “dark”, “dirt”, “neon”, “mint”, “plum”, “sunrise”.
Note: If you have made edits to the theme’s CSS files be sure to update /assets/css/main.scss to include@import "minimal-mistakes/skins/default"; // skin before the minimal-mistakes import.
Site locale
site.locale is used to declare the primary language for each web page within the site.
Example: locale: "en-US" sets the lang attribute for the site to the United States flavor of English, while en-GB would be for the United Kingdom style of English. Country codes are optional and the shorter variation locale: "en" is also acceptable. To find your language and country codes check this reference table.
Properly setting the locale is important for associating localized text found in the UI Text data file. An improper match will cause parts of the UI to disappear (eg. button labels, section headings, etc).
Note: The theme comes with localized text in English (en, en-US, en-GB). If you change locale in _data/site.yml to something else, most of the UI text will go blank. Be sure to add the corresponding locale key and translated text to _data/ui-text.yml to avoid this.
Site title
The name of your site. Is used throughout the theme in places like the site masthead and <title> tags.
Example: title: "My Awesome Site"
You also have the option of customizing the separation character used in SEO-friendly page titles.
Example: title_separator: "|" would produce page titles like Sample Page | My Awesome Site.
Note: Long site titles have been known to break the masthead layout. Avoid adding a long “tagline” to the title to prevent this from happening, e.g. My Awesome Site is the Best Because I Say So.
Site subtitle
A short tagline that appears below the title in site masthead.
Example: subtitle: "Version 2.0"
Site name
Used to assign a site author. Don’t worry, you can override the site author with different ones on specific posts, pages, or collection documents.
Example: name: "Michael Rose".
ProTip: If you want to get crafty with your YAML you can use anchors to reuse values. For example foo: &var "My String" allows you to reuse "My String" elsewhere in _data/site.yml like so… bar: *var. You’ll see a few examples of this in the provided config.
Site description
Fairly obvious. site.description describes the site. Used predominantly in meta descriptions for improving SEO.
Example: description: "A flexible 11ty theme for your blog or site with a minimalist aesthetic."
Site URL
The base hostname and protocol for your site. If you’re hosting on GitHub Pages this will be something like url: "https://mmistakes.github.io" or url: "https://mademistakes.com" if you have a custom domain name.
GitHub Pages now forces https:// for new sites so be mindful of that when setting your URL to avoid mixed-content warnings.
Site base URL and pathPrefix
This little option causes all kinds of confusion in the 11ty community. If you’re not hosting your site as a GitHub Pages Project or in a subfolder (eg: /blog), then don’t mess with it.
In the case of the Minimal Mistakes demo site it’s hosted on GitHub at https://mmistakes.github.io/minimal-mistakes. To correctly set this base path I’d use url: "https://mmistakes.github.io" and pathPrefix: "/minimal-mistakes" setting in eleventy.js or use it as a parameter on runtime…
Site scripts
Add scripts to the <head> or closing </body> elements by assigning paths to either head_scripts and/or footer_scripts.
For example, to add a CDN version of jQuery to page’s head along with a custom script you’d do the following:
head_scripts:
- https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.2.1.min.js
- /assets/js/your-custom-head-script.jsConsult the JavaScript documentation for more information on working with theme scripts.
Site default teaser image
To assign a fallback teaser image used in the “Related Posts” module, place a graphic in the /assets/images/ directory and add the filename to _data/site.yml like so:
teaser: /assets/images/placeholder/500x300.pngThis image can be overridden at anytime by applying the following to a document’s YAML Front Matter.
header:
teaser: /assets/images/my-awesome-post-teaser.jpg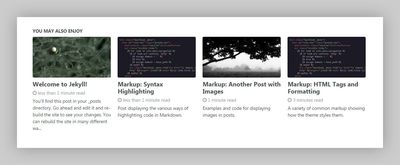
Site masthead logo
To insert a logo before the site title, place a graphic in the /assets/images/ directory and add the filename to _data/site.yml:
logo: "/assets/images/88x88.png"
Site masthead title
By default your site title is used in the masthead. You can override this text by adding the following to your _data/site.yml:
masthead_title: "My Custom Title"Site RTL direction
site.rtl is used to turn the direction of the page into right to left. This option can be used for RTL languages (like Arabic, Persian, etc)
Example: rtl: true sets the direction of the page to right to left. By default this option is rtl: false.
Breadcrumb navigation (beta)
Enable breadcrumb links to help visitors better navigate deep sites. Because of the fragile method of implementing them they don’t always produce accurate links reliably. For best results:
- Use a category based permalink structure e.g.
permalink: /:categories/:title/ - Manually create pages for each category or use a Zero Maintenance Tag Pages for your Blog to auto-generate them. If these pages don’t exist breadcrumb links to them will be broken.
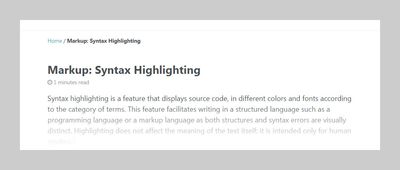
breadcrumbs: true # disabled by defaultBreadcrumb start link text and separator character can both be changed in the UI Text data file.
Post dates
Enable post date snippets with show_date: true in YAML Front Matter.
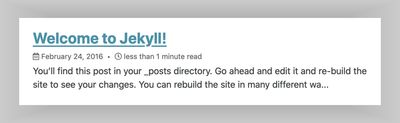
Instead of adding show_date: true to each post, apply as a default in _data/site.yml like so:
defaults:
# _posts
- scope:
path: ""
type: posts
values:
show_date: trueTo disable post date for a post, add show_date: false to its YAML Front Matter, overriding what was set in _data/site.yml.
When dates are shown on blog posts or pages, a date format will be chosen to format the date string. The default format is "%B %-d, %Y", which will be displayed like “February 24, 2016”. You can choose your date format by referencing this cheat sheet. For example, use your date format in _data/site.yml.
date_format: "%Y-%m-%d"Reading time
Enable estimated reading time snippets with read_time: true in YAML Front Matter. 200 has been set as the default words per minute value which can be changed by adjusting words_per_minute: in _data/site.yml.
Instead of adding read_time: true to each post, apply as a default in _data/site.yml like so:
defaults:
# _posts
- scope:
path: ""
type: posts
values:
read_time: trueTo disable reading time for a post, add read_time: false to its YAML Front Matter to override what was set in _data/site.yml.
words_per_minute can also be adjusted on a per-page basis by adding to its YAML Front Matter. This is useful for sites with multi-lingual content where you’d like specify a different value from the site config.
words_per_minute: 250Page meta separator
To customise the separator between the page date and reading time (if both are enabled), edit .page__meta-sep::before in a custom stylesheet.
For example,
.page__meta-sep::before {
content: "\2022";
padding-left: 0.5em;
padding-right: 0.5em;
}Code block copy button
New in v4.26.0
To enable a copy button on code blocks, add the following to _data/site.yml:
enable_copy_code_button: trueWhen enabled site-wide, the button can be disabled on individual code blocks by adding no-copy to the code block’s class list.
```
Hey, I have a "copy to clipboard" button!
``````
But I don't have one.
```
{: .no-copy}Comments
Disqus, Discourse, Facebook, utterances, giscus and static-based commenting via Staticman are built into the theme. First set the comment provider you’d like to use:
| Name | Comment Provider |
|---|---|
| disqus | Disqus |
| discourse | Discourse |
| Facebook Comments | |
| staticman_v2 | Staticman v2 / v3 |
| staticman | Staticman v1 (deprecated) |
| utterances | utterances |
| giscus | giscus |
| custom | Other |
Then add comments: true to each document you want comments visible on.
Instead of adding YAML Front Matter to each document, apply as a default in _data/site.yml. To enable comments for all posts:
defaults:
# _posts
- scope:
path: ""
type: posts
values:
comments: trueIf you add comments: false to a post’s YAML Front Matter it will override the default and disable comments for just that post.
Note: Comments are disabled in development. To enable when testing/building locally be sure to set
ELEVENTY_ENV=production to force the environment to production.
Disqus
To use Disqus you’ll need to create an account and shortname. Once you have both update _data/site.yml to:
comments:
provider: "disqus"
disqus:
shortname: "your-disqus-shortname"Discourse
For guidance on how to set up Discourse for embedding comments from a topic on a post page, consult this guide.
comments:
provider: "discourse"
discourse:
server: # meta.discourse.orgNote: Do not include http:// or https:// when setting your Discourse server. The theme automatically prepends the URL //, following a scheme-less pattern.
Facebook comments
To enable Facebook Comments choose how many comments you’d like visible per post and the color scheme of the widget.
comments:
provider: "facebook"
facebook:
appid: # optional
num_posts: # 5 (default)
colorscheme: # "light" (default), "dark"utterances comments
To use utterances you will need to install the app to your GitHub repository by adding the following to _data/site.yml:
repository: # GitHub username/repo-name e.g. "mmistakes/minimal-mistakes"Note: Make sure the repo is public, otherwise your readers will not be able to view the issues/comments. The issues feature also needs to be active on your repo.
To enable utterances on the front end set comments.provider and the color theme of the widget.
comments:
provider: "utterances"
utterances:
theme: "github-light" # "github-dark"
issue_term: "pathname"
label: "comment" # Optional - must be existing label.giscus comments
To use giscus you will need to install the app to your GitHub repository.
The next step is to go to https://giscus.app and fill out the desired settings. This will generate JavaScript that will provide you with the settings you will need to configure things below.
You’ll need to ensure you’ve added the following to _data/site.yml:
repository: # GitHub username/repo-name e.g. "mmistakes/minimal-mistakes"Note: Make sure the repo is public, otherwise your readers will not be able to view the issues/comments. The discussions feature also needs to be active on your repo.
To enable giscus on the front end set comments.provider and the other additional options.
comments:
provider: "giscus"
giscus:
repo_id : # Shown during giscus setup at https://giscus.app
category_name : # Full text name of the category
category_id : # Shown during giscus setup at https://giscus.app
discussion_term : # "pathname" (default), "url", "title", "og:title"
reactions_enabled : # '1' for enabled (default), '0' for disabled
theme : # "light" (default), "dark", "dark_dimmed", "transparent_dark", "preferred_color_scheme"Static-based comments via Staticman
Transform user comments into _data files that live inside of your GitHub repository by enabling Staticman.
Note: Please note that as of September 2018, Staticman is reaching GitHub API limits due to its popularity, and it is recommended by its maintainer that users deploy their own instances for production (use site.staticman.endpoint). Consult the Staticman “Get Started” guide for more info.
Add Staticman as a collaborator on GitHub (legacy)
- Allow Staticman push access to your GitHub repository by clicking on Settings, then the Collaborators tab and adding your GitHub bot as a collaborator.
- To accept the pending invitation visit:
https://{your Staticman v2/3 API}/v[2|3]/connect/{your GitHub username}/{your repository name}.
Note: The new GitHub App authentication method is recommended for GitHub repositories to avoid the API rate limit.
Configure Staticman
Staticman v3
Due to the support for GitLab, the URL scheme has been changed. Between v3/entry/ and /{your Git username}, one needs to input a Git service provider (either github or gitlab). For example
https://{your Staticman v3 API}/v3/entry/github/{your Git username}/{your repository name}/…
# _data/site.yml (defaults)
repository : # Git username/repo-name e.g. "mmistakes/minimal-mistakes"
comments:
provider : "staticman_v2"
staticman:
branch : "master"
endpoint : https://{your Staticman v3 API}/v3/entry/github/Staticman v2
Default settings have been provided in staticman.yml and are commented to guide you through setup. View the full list of configurations.
# staticman.yml (defaults)
comments:
allowedFields : ["name", "email", "url", "message"]
branch : "master"
commitMessage : "New comment by {fields.name}"
filename : "comment-{@timestamp}"
format : "yaml"
generatedFields:
date:
type : "date"
options:
format : "iso8601"
moderation : true
path : "_data/comments/{options.slug}"
requiredFields : ["name", "email", "message"]
transforms:
email : md5These settings need to be added to your _data/site.yml file as well:
# _data/site.yml (defaults)
repository : # GitHub username/repo-name e.g. "mmistakes/minimal-mistakes"
comments:
provider : "staticman_v2"
staticman:
branch : "master"Branch setting: This is the branch comment files will be sent to via pull requests. If you host your site on GitHub Pages it will likely be master unless your repo is setup as a project — use gh-pages in that case.
Note: Staticman is currently compatible with GitHub and GitLab based repositories. Support for GitLab Pages is already available at Staticman v3.
Staticman v1 (deprecated)
Default settings have been provided in _data/site.yml. The important ones to set are provider: "staticman", branch, and path. View the full list of configurations.
# _data/site.yml (defaults)
comments:
provider: "staticman"
staticman:
allowedFields : ['name', 'email', 'url', 'message']
branch : "master"
commitMessage : "New comment by {fields.name}"
filename : comment-{@timestamp}
format : "yml"
moderation : true
path : "_data/comments/{options.slug}"
requiredFields : ['name', 'email', 'message']
transforms:
email : "md5"
generatedFields:
date:
type : "date"
options:
format : "iso8601" # "iso8601" (default), "timestamp-seconds", "timestamp-milliseconds"Comment moderation
By default comment moderation is enabled in staticman.yml. As new comments are submitted Staticman will send a pull request. Merging these in will approve the comment, close the issue, and automatically rebuild your site (if hosted on GitHub Pages).
To skip this moderation step simply set moderation: false.
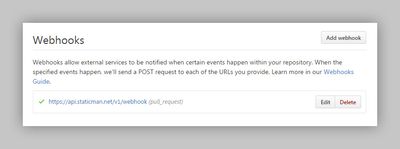
ProTip: Create a GitHub webhook that sends a POST request to the following payload URL https://{your Staticman API URL}/v2/webhook and triggers a “Pull request” event to delete Staticman branches on merge.
reCAPTCHA support (v2 only)
To enable Google’s reCAPTCHA to aid in spam detection you’ll need to:
- Apply for reCAPTCHA API keys and register your site using the reCAPTCHA V2 type.
- Add your site and secret keys to
staticman.ymland_data/site.yml. Be sure to properly encrypt your secret key using Staticman’s encrypt endpoint.
reCaptcha:
enabled: true
siteKey: # "6LdRBykTAAAAAFB46MnIu6ixuxwu9W1ihFF8G60Q"
secret: # "PznnZGu3P6eTHRPLORniSq+J61YEf+A9zmColXDM5icqF49gbunH51B8+h+i2IvewpuxtA9TFoK68TuhUp/X3YKmmqhXasegHYabY50fqF9nJh9npWNhvITdkQHeaOqnFXUIwxfiEeUt49Yoa2waRR7a5LdRAP3SVM8hz0KIBT4="Other comment providers
To use another provider not included with the theme set provider: "custom" then add their embed code to _includes/comments-providers/custom.html.
Custom feed URL
There is no builtin feed for the theme at the moment.
To link to an externally hosted feed update atom_feed in _data/site.yml like so:
atom_feed:
path: "http://feeds.feedburner.com/youFeedname"Note: By default the site feed is linked in two locations: inside the <head> element and at the bottom of every page in the site footer.
Disable Feed Icons
To remove the RSS icon in the header and footer, update atom_feed in _data/site.yml like so:
atom_feed:
hide: trueSite search
To enable site-wide search add search: true to your _data/site.yml.
Lunr (default)
The default search uses Lunr to build a search index of all post and your documents in collections. This method is 100% compatible with sites hosted on GitHub Pages.
To have it index all pages, update lunr in _data/site.yml like so:
lunr:
search_within_pages: trueNote: Only the first 50 words of a post or page’s body content is added to the Lunr search index. Setting search_full_content to true in your _data/site.yml will override this and could impact page load performance.
Algolia
If you want to use Algolia, you can checkout this guide.
-
Switch search providers from
lunrtoalgoliain your_data/site.ymlfile:search_provider: algolia -
Add the following Algolia credentials to your
_data/site.ymlfile. If you don’t have an Algolia account, you can open a free Community plan. Once signed in, you can grab your credentials from your dashboard.algolia: application_id: # YOUR_APPLICATION_ID index_name: # YOUR_INDEX_NAME search_only_api_key: # YOUR_SEARCH_ONLY_API_KEY powered_by: # true (default), false
Please help expand these docs, if you get Algolia running on your own site.
Google Custom Search Engine
Add a Google search box to your site.
-
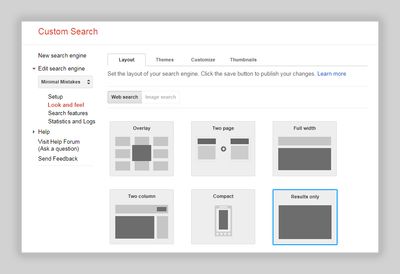
Create a New search engine in Google Custom Search Engine, give it an appropriate name and setup “Sites to search” to your liking.
-
Under Look and feel choose the “Results only” layout and a theme (Minimalist is a good choice to match the default look of the Minimal Mistakes).
-
Select “Save & Get Code” and grab your search engine ID from the line that begins with
var cx = 'YOUR_SEARCH_ENGINE_ID'. -
Add your search engine ID to
_data/site.ymllike so:google: search_engine_id: YOUR_SEARCH_ENGINE_ID
Note: If your site is new and hasn’t been indexed by Google yet, search will be incomplete and won’t provide accurate results.
SEO, social sharing, and analytics settings
All optional, but a good idea to take the time setting up to improve SEO and links shared from the site.
Google Search Console
Formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, add your verification code like so: google_site_verification: "yourVerificationCode".
Note: You likely won’t have to do this if you verify site ownership through Google Analytics instead.
Bing Webmaster Tools
There are several ways to verify site ownership — the easiest adding an authentication code to your config file.
Copy and paste the string inside of content:
<meta name="msvalidate.01" content="0FC3FD70512616B052E755A56F8952D" />Into _data/site.yml
bing_site_verification: "0FC3FD70512616B052E755A56F8952D"Naver Webmaster Tools
To verify site ownership you will need to create a Naver account and then Add your site via Naver Webmaster Tools.
Much like Google and Bing you’ll be provided with a meta description:
<meta name="naver-site-verification" content="6BF5A01C0E650B479B612AC5A2184144">`Which you can add to your _data/site.yml like so:
naver_site_verification: "6BF5A01C0E650B479B612AC5A2184144"Yandex
To verify site ownership copy and paste the string inside of content:
<meta name='yandex-verification' content='2132801JL' />Into _data/site.yml
yandex_site_verification: "2132801JL"Baidu
There are several ways to verify site ownership — the easiest is adding an authentication code to your config file.
Copy and paste the string inside of content:
<meta name="baidu-site-verification" content="code-iA0wScWXN1" />Into _data/site.yml
baidu_site_verification: "code-iA0wScWXN1"Twitter Cards and Facebook Open Graph
To improve the appearance of links shared from your site to social networks like Twitter and Facebook be sure to configure the following.
Site Twitter username
Twitter username for the site. For pages that have custom author Twitter accounts assigned in their YAML Front Matter or data file, they will be attributed as a creator in the Twitter Card.
For example if my site’s Twitter account is @mmistakes-theme I would add the following to _data/site.yml
twitter:
username: "mmistakes-theme"And if I assign @mmistakes as an author account it will appear in the Twitter Card along with @mmistakes-theme, attributed as a creator of the page being shared.
Note: You need to validate cards are working and have Twitter approve Player Cards before they begin showing up.
Facebook Open Graph
If you have a Facebook ID or publisher page add them:
facebook:
app_id: # A Facebook app ID
publisher: # A Facebook page URL or ID of the publishing entityWhile not part a part of Open Graph, you can also add your Facebook username for use in the sidebar and footer.
facebook:
username: "michaelrose" # https://www.facebook.com/michaelroseProTip: To debug Open Graph data use this tool to test your pages. If content changes aren’t reflected you will probably have to hit the Scrape Again button to refresh.
Open Graph default image
For pages that don’t have a header.image assigned in their YAML Front Matter, site.og_image will be used as a fallback. Use your logo, icon, avatar or something else that is meaningful. Just make sure it is placed in the /assets/images/ folder, has a minimum size of 120px by 120px, and is less than 1MB in file size.
og_image: /assets/images/site-logo.png
```<figure class=""><img src="/assets/images/mm-twitter-card-summary-image.jpg"
alt="Twitter Card summary example"><figcaption>
Example of an image placed in a Summary Card.
</figcaption></figure>
Documents who have a `header.image` assigned in their YAML Front Matter will appear like this when shared on Twitter and Facebook.<figure class=""><img src="/assets/images/mm-twitter-card-summary-large.jpg"
alt="page shared on Twitter"><figcaption>
Shared page on Twitter with header image assigned.
</figcaption></figure>
<figure class=""><img src="/assets/images/facebook-share-example.jpg"
alt="page shared on Facebook"><figcaption>
Shared page on Facebook with header image assigned.
</figcaption></figure>
##### Include your social profile in search results
Use markup on your official website to add your [social profile information](https://developers.google.com/structured-data/customize/social-profiles#adding_structured_markup_to_your_site) to the Google Knowledge panel in some searches. Knowledge panels can prominently display your social profile information.
```yaml
social:
type: # Person or Organization (defaults to Person)
name: # If the user or organization name differs from the site's name
links:
- "https://twitter.com/yourTwitter"
- "https://www.facebook.com/yourFacebook"
- "https://instagram.com/yourProfile"
- "https://www.linkedin.com/in/yourprofile"Analytics
Analytics is disabled by default. To enable globally select one of the following:
| Name | Analytics Provider |
|---|---|
| Google Standard Analytics | |
| google-universal | Google Universal Analytics |
| google-gtag | Google Analytics Global Site Tag |
| custom | Other analytics providers |
For Google Analytics add your Tracking Code:
analytics:
provider: "google-gtag"
google:
tracking_id: "UA-1234567-8"
anonymize_ip: false # defaultTo use another provider not included with the theme set provider: "custom" then add their embed code to _includes/analytics-providers/custom.html.
Note: Analytics are disabled in development. To enable when testing/building locally be sure to set
ELEVENTY_ENV=production to force the environment to production.
Site author
Used as the defaults for defining what appears in the author sidebar.
Note: For sites with multiple authors these values can be overridden post by post with custom YAML Front Matter and a data file. For more information on how that works see below.
author:
name : "Your Name"
avatar : "/assets/images/bio-photo.jpg"
bio : "My awesome biography constrained to a sentence or two goes here."
location : "Somewhere, USA"Author links are all optional, include the ones you want visible under the author.links array.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| label | Link label (e.g. "Twitter") |
| icon | Font Awesome icon classes (e.g. "fab fa-fw fa-twitter-square") |
| url | Link URL (e.g. "https://twitter.com/mmistakes") |
author:
name: "Your Name"
avatar: "/assets/images/bio-photo.jpg"
bio: "I am an **amazing** person." # Note: Markdown is allowed
location: "Somewhere"
links:
- label: "Made Mistakes"
icon: "fas fa-fw fa-link"
url: "https://mademistakes.com"
- label: "Twitter"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-twitter-square"
url: "https://twitter.com/mmistakes"
- label: "GitHub"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-github"
url: "https://github.com/mmistakes"
- label: "Instagram"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-instagram"
url: "https://instagram.com/mmistakes"To customize the author sidebar, read the full layout documentation.
Site footer
Footer links can be added under the footer.links array.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| label | Link label (e.g. "Twitter") |
| icon | Font Awesome icon classes (e.g. "fab fa-fw fa-twitter-square") |
| url | Link URL (e.g. "https://twitter.com/mmistakes") |
footer:
links:
- label: "Twitter"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-twitter-square"
url: "https://twitter.com/mmistakes"
- label: "GitHub"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-github"
url: "https://github.com/mmistakes"
- label: "Instagram"
icon: "fab fa-fw fa-instagram"
url: "https://instagram.com/mmistakes"Note: Twitter and Facebook footer links no longer automatically pull from site.twitter.username and site.facebook.username. This behavior has been deprecated in favor of the footer.links array above.
To change “Follow:” text that precedes footer links, edit the follow_label key in _data/ui-text.yml.
Reading files
In eleventy.js you can pass files through for the main site. Check out the demo.
in .eleventyignore you can write which files to ignore when building the site.
Front Matter Defaults
To save yourself time setting Front Matter Defaults for posts, pages, and collections is the way to go. Sure you can assign layouts and toggle settings like reading time, comments, and social sharing in each file, but that’s not ideal.
Using directory specific datafiles, you can set layout layout and enable author profiles, reading time, comments, social sharing, and related posts for all posts — in one shot. Like this in _posts/_posts.json.
{
"layout": "single",
"author_profile": true,
"read_time": true,
"comments": true,
"share": true,
"related": true
}Pages Front Matter defaults can be scoped like this in _pages/_pages.json:
{
"layout": "single"
}And of course any default value can be overridden by settings in a post, page, or collection file. All you need to do is specify the settings in the YAML Front Matter. For more examples be sure to check out the demo site’s _posts/_posts.json.
Outputting
You control the outputting via permalinks. Dive into the 11ty documentation on permalinks.
Paginate
Everything about pagination has not been setup by default. Please help set it up and expand on these docs.
Timezone
This sets the timezone environment variable, which Ruby uses to handle time and date creation and manipulation. Any entry from the IANA Time Zone Database is valid. The default is the local time zone, as set by your operating system.
timezone: America/New_YorkArchive settings
The theme ships with support for taxonomy (category and tag) pages. GitHub Pages hosted sites need to use a Liquid only approach.
The default type is set to use Liquid.
This would create category and tag links in the breadcrumbs and page meta like: /categories/#foo and /tags/#foo.
Note: these are simply hash (fragment) links into the full taxonomy index pages. For them to resolve properly, the category and tag index pages need to exist at /categories/index.html (copy to _pages/category-archive.md) and /tags/index.html (copy to _pages/tag-archive.md).
You can also look into Zero Maintenance Tag Pages for your Blog to generate these pages automatically.
HTML compression
If you care at all about performance (and really who doesn’t) compressing the HTML files is a good thing to do.
Please help expand this documentation, if you know how to do this with npm or 11ty directly.
Note: CDN services such as CloudFlare provide optional automatic minification for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. If you are serving your site via such a service and have minification enabled, this configuration might be redundant.